As the world of data engineering is evolving rapidly, one thing that data teams still find difficult to decide how to process and deliver data. Should they do it in batches, stream it, or use a hybrid approach? This is today’s data engineer’s dilemma.
Remember, this i’t just a technical choice but also demonstrates the team’s importance and core values regarding timeliness, complexity, and accuracy.
Every method has its own benefits and trade-offs, and therefore, it is very important to understand its fundamental concepts so that you can design efficient pipelines supporting business needs.
So, the biggest data engineer’s dilemma is not choosing the right approach but balancing competing priorities, i.e., how quickly you need insights, how complex your systems can be, and how reliable the results must be. Let’s dive deeper and understand these approaches and their trade-offs.
Understanding Batch, Stream, and Hybrid Approach
1. Batch Processing: Complete and Predictable
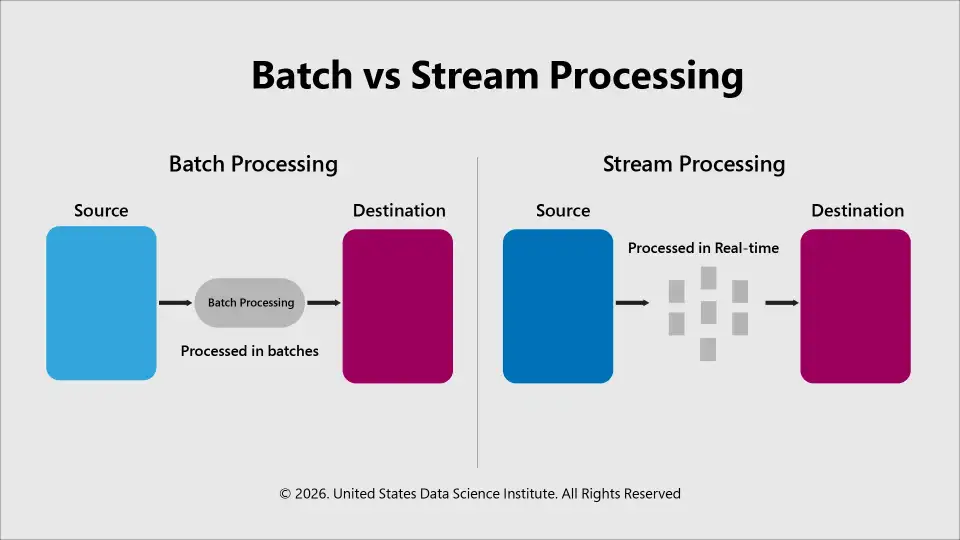
As the name suggests, this method involves collecting data over a period and processing it all at once at regular intervals.
For example, preparing a daily report. In this, first you gather all the inputs/data and then run your analysis.
This method is very useful when you need completeness over speed, and real-time updates are not so important.
Advantages of Batch Processing
Limitations of Batch Processing
Use Cases
This type of processing approach is most widely used for nightly ETL jobs, historical data analytics, regulatory reporting, and large-scale transformations where immediate insights are not essential.
2. Stream Processing: Immediate but Complex
This is another method a data engineer’s Journey entails. The stream processing approach treats data as a continuous flow. Be it a user click, sensor reading, transaction, or any other event, the system processes it as it arrives in real time.
Advantages of Stream Processing
Limitations
Though stream processing is great for speed and instant insights, it increases architectural complexity as well as operational effort.
Use cases
Stream processing is widely used in areas requiring real-time insights, like anomaly detection, live analytics dashboards, recommendation engines, and data science decision-making opérations.
Streaming use cases such as real-time fraud detection, predictive analytics, and operational dashboards are cited by over 70% of enterprises that prioritize streaming investments (source: Global Growth Insights).
3. Hybrid Architecture: Best of Both
Batch and stream processing aren’t sufficient in themselves. Not all problems fit neatly into these categories. This is where the hybrid approach becomes a savior. It combines elements of both processing types and helps balance timeliness, accuracy, and ease of operation.
Hybrid design works on a simple principle that data quality and readiness evolve over time. First, the data is processed quickly in a streaming layer that provides users with early insights. Then, a more thorough batch processing occurs that corrects the results for final consistency.
Two common principles of hybrid approaches are the Lambda and Kappa architectures.
Data engineers use this hybrid solution to get data at the right time so that they can assist with data-driven decision-making.
Dimensions of the Trade-Off
The following things are considered while choosing the right approach: batch, stream, or hybrid.
First, determine how quickly your consumers need insights. If they require instant updates for their projects, consider streaming data. And if they are ready to accept a delay of minutes or hours, you can go for batch processing.
As mentioned, streaming systems are quite difficult. A great expertise is required to select tools like Kafka, Flink, or Spark Structured Streaming and build reliable data pipelines. On the other hand, batch systems are simple as each run starts from a known state.
Cloud-based streaming platforms are now used by nearly 71% of organizations due to scalability and flexible deployment, reported Global Growth Insights.
Since the entire dataset is processed at once in batch processing, it provides a better and more consistent view. Whereas streaming initially provides approximate or partial results, and with backfills/reconciliation steps, provides better results finally at later stages.
At last, the final choice depends on the organization’s capabilities. Those who are comfortable with distributed systems and continuous operations can benefit from streaming while those who want a simple and auditable processing can go for a batch processing approach.
Solving Data Engineer’s Dilemma – Pick the Right Decision Framework
Data engineers’ journey often involves making the right decision, whether to select a stream, batch, or hybrid approach. So, here is a simplified way to make the right decision:
Consider streaming or hybrid
Batch processing would be enough
Go for batch processing and hybrid with backfills
If not, then batch processing could be ideal, and a carefully implemented hybrid approach can also be used.
Final Thoughts!
If data engineers are getting so many options to process data, then they must also understand that no approach is right or wrong. Each of them has its own strengths, limitations, and purposes. Choosing the right approach can be a difficult choice. So, you can follow the decision framework mentioned above.
Remember, the right choice depends upon business priorities and operational capacity and not just on types of data.
So, instead of discussing which technology is better, focus on “what insights your projects aim for and how quickly you want them?” When you have the answer, you have the right choice!
This website uses cookies to enhance website functionalities and improve your online experience. By clicking Accept or continue browsing this website, you agree to our use of cookies as outlined in our privacy policy.